Umbilical cord tissue is a rich, ethically unproblematic source of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs).
Mechanical dissociation with the TissueGrinder enables fast, standardized isolation without enzymes – maintaining viability and surface characteristics for robust culture and downstream analysis.
Reference: Stange K., Wolter T., Fu Z., Burdeos G., Mideksa Y., Friese A., Röntgen M. (2025). Isolation of Porcine Umbilical Cord Cells by Mechanical Tissue Dissociation Using a Tissue Grinder. Cells 14, 1425. doi:10.3390/cells14181425.
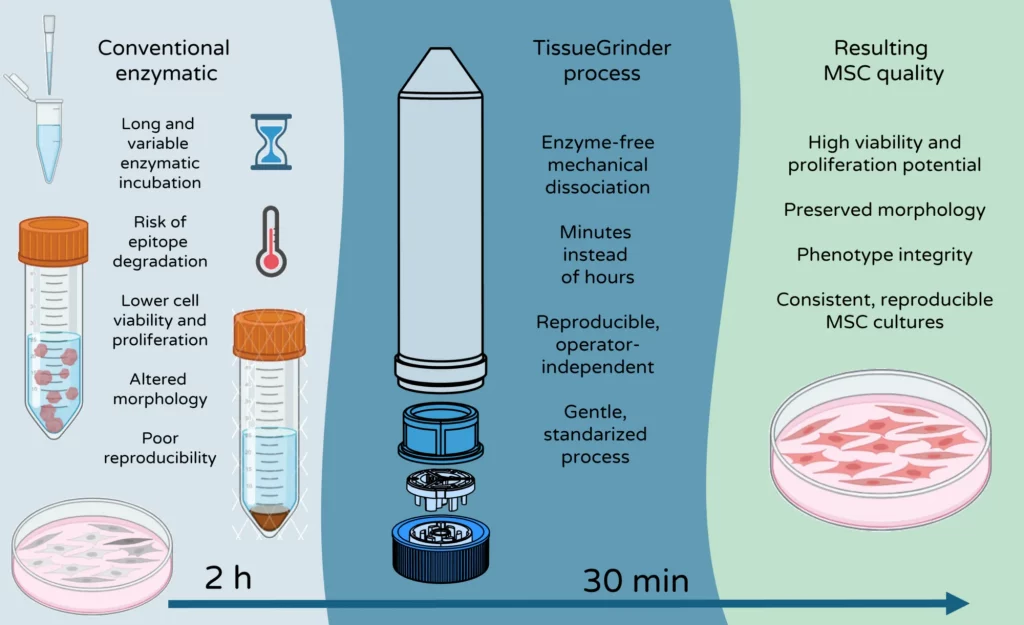
Fresh umbilical cord segments are mechanically dissociated in the TissueGrinder (100 µm filter). Cells are pelleted and seeded for MSC culture expansion (P1–P3). The study used porcine cords as a model analogous to human tissue.
Cells isolated with the TissueGrinder adhered and proliferated through multiple passages (P1–P3), displayed typical spindle-shaped MSC morphology, and reached confluence within days. Mechanical dissociation preserved high viability and yielded performance comparable or superior to enzymatic digestion.